What is Cloud Computing?
“Cloud computing” (also called simply, “the cloud”) describes the act of storing, managing and processing data online — as opposed to on your own physical computer or network.
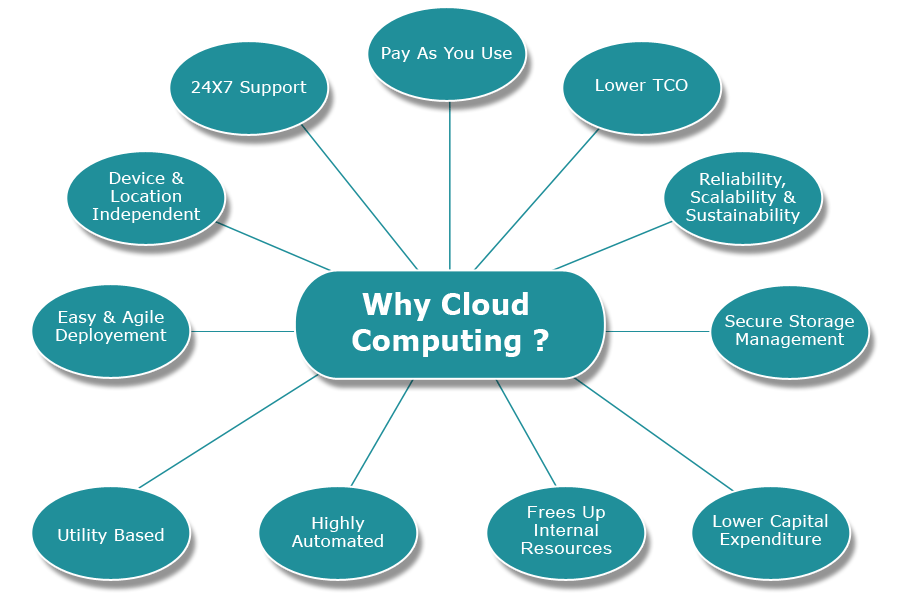
Features
Types of Clouds
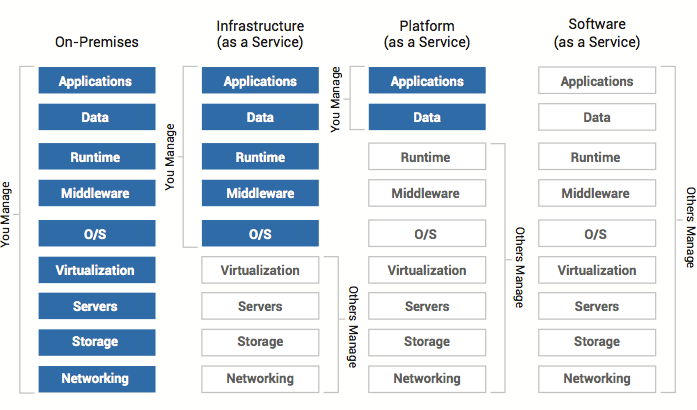
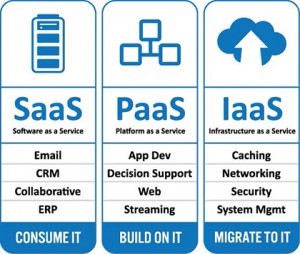
| Type | Description | Uses | Example |
| Software as a Service (SaaS) | Cloud application services, SaaS, represent the largest cloud market and are still growing quickly. SaaS uses the web to deliver applications that are managed by a third-party vendor and whose interface is accessed on the clients’ side. Most SaaS applications can be run directly from a web browser without any downloads or installations required, although some require plugins. | Replaces traditional on-device software | Google Apps, Salesforce, Workday, Concur, Citrix GoToMeeting, Cisco WebEx, Microsoft Office 365 |
| Platform as a Service (PaaS) | Cloud platform services, or PaaS, are used for applications, and other development, while providing cloud components to software. What developers gain with PaaS is a framework they can build upon to develop or customize applications. PaaS makes the development, testing, and deployment of applications quick, simple, and cost-effective. With this technology, enterprise operations, or a third-party provider, can manage OSes, virtualization, servers, storage, networking, and the PaaS software itself. Developers, however, manage the applications. | Increases developer productivity and utilization rates while also decreasing an application’s time-to-market | Apprenda |
| Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) | Cloud infrastructure services, known as IaaS, are self-service models for accessing, monitoring, and managing remote datacenter infrastructures, such as compute (virtualized or bare metal), storage, networking, and networking services (e.g. firewalls). Instead of having to purchase hardware outright, users can purchase IaaS based on consumption, similar to electricity or other utility billing. | Extends current data center infrastructure for temporary workloads (e.g. increased Christmas holiday site traffic) | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google, AliCloud |
Why Use Cloud Services?
Reduce IT Manpower to manage IT Infrastructure
– A lot of time is required to manage an in-house mail server
– To trace and resolve false positive email, spam issues, non-delivery
– To archive email for user mailbox
2) Focus on Service Delivery rather than Supporting Infrastructure
3) Focus on OPEX rather than CAPEX (can lead to better budgeting)
4) Dynamic to business requirement changes (ie manpower, high peak seasonal usage) Highly scalable
5) Optimized Use of Hardware – Support Green Movement, reduce carbon footprint
6) No need to worry about downtime (maintenance, electric testing, hardware compatibility issues, hardware failure)
7) No need to worry about software licensing compliance
8) More secured than most on-premises server room or co-managed datacentre
9) No need to worry about products or service been obselete
10) No need to worry about hardware replacement after warranty period
11) No need to think about future upgrades. Version Upgrades are scheduled and seamlessly performed in the background.
12) No need to worry about single point of failure.
– Redundant Power Supply for Server, Secondary WAN, Firewall running high-availability (HA)
13) Office Relocation is easier and painless
14) Readiness for Disaster Recovery
15) Lower Operational Cost – can outsource IT Support easily
16) Freed up valuable office space for Server Room
![]()
Win-Pro Consultancy Pte Ltd © Copyright 2017 Terms of Service & Privacy Policy